Hydrogen Fuel Cells in US Transportation: A 2025 Status Report

Hydrogen fuel cells hold promise for revolutionizing US transportation by 2025, offering zero-emission solutions for various sectors like heavy-duty trucking, public transit, and even personal vehicles, though challenges in infrastructure and cost remain.
Will hydrogen fuel cells power the future of US transportation? A 2025 status report reveals the technology’s potential to transform how we move, offering a cleaner, more sustainable alternative to traditional fossil fuels.
Hydrogen Fuel Cell Technology: An Overview for 2025
Hydrogen fuel cell technology has emerged as a promising contender in the race to decarbonize the transportation sector. By 2025, advancements and growing interest fuel its potential impact.
But what exactly are hydrogen fuel cells, and why are they gaining traction?
How Hydrogen Fuel Cells Work
Hydrogen fuel cells convert the chemical energy of hydrogen into electricity through a chemical reaction with oxygen. This process produces only water and heat as byproducts, making it a zero-emission technology at the point of use.
Advantages of Hydrogen Fuel Cells
Compared to traditional combustion engines, hydrogen fuel cells offer several advantages: higher efficiency, reduced greenhouse gas emissions, and quieter operation. When compared to battery electric vehicles, fuel cell vehicles offer longer ranges and faster refueling times.
- Zero Emissions: Operates with no harmful emissions.
- High Efficiency: Converts fuel to energy more efficiently than combustion engines.
- Longer Range: Provides greater range compared to battery-electric vehicles in some applications.
As of 2025, while hydrogen fuel cell technology holds significant promise, challenges remain in terms of infrastructure development and cost reduction.
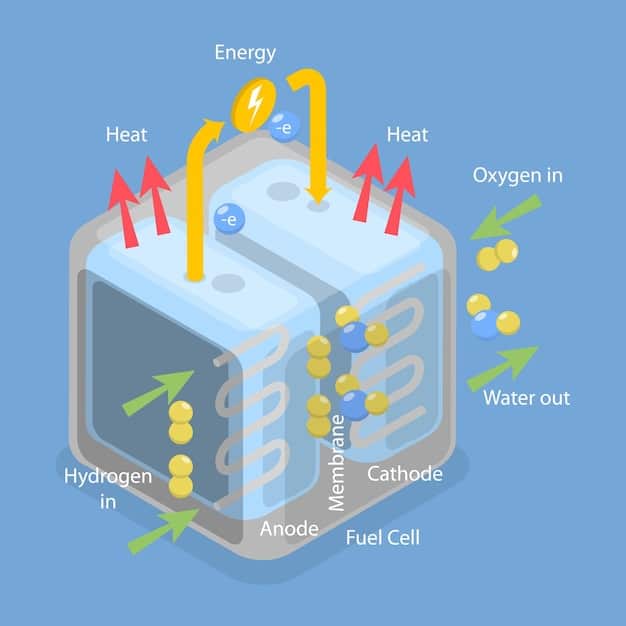
Current State of Hydrogen Infrastructure in the US
A widespread network of hydrogen refueling stations is crucial for the widespread adoption of hydrogen fuel cell vehicles. As of 2025, the hydrogen infrastructure in the US is still in its early stages of development.
Significant progress has been made, but challenges persist.
Existing Hydrogen Refueling Stations
Currently, most hydrogen refueling stations are located in California, driven by the state’s strong support for zero-emission vehicles. Other states are beginning to invest in hydrogen infrastructure, but the coverage remains limited.
Challenges in Infrastructure Development
Building a comprehensive hydrogen infrastructure requires significant investment in production, storage, and distribution. The high cost of building refueling stations and the lack of economies of scale continue to be obstacles.
- High Costs: Infrastructure development is expensive.
- Limited Coverage: Refueling stations are concentrated in specific regions.
- Production and Distribution: Challenges in scaling up hydrogen production and ensuring efficient distribution.
While these challenges are significant, ongoing research and development efforts are focused on reducing costs and improving the efficiency of hydrogen production and distribution. Government incentives and private investment will play a crucial role in expanding the hydrogen infrastructure in the US.
Hydrogen Fuel Cells for Heavy-Duty Transportation
Heavy-duty vehicles, such as trucks and buses, are major contributors to air pollution and greenhouse gas emissions. Hydrogen fuel cells offer a compelling solution for decarbonizing this sector.
They can deliver long ranges and fast refueling capabilities.
Advantages in Heavy-Duty Applications
Hydrogen fuel cell trucks and buses can achieve longer ranges compared to their battery-electric counterparts, making them suitable for long-haul transportation. Fast refueling times minimize downtime, which is crucial for commercial operations.
Pilot Projects and Deployments
Several pilot projects are underway in the US, testing the feasibility of hydrogen fuel cell trucks and buses in real-world conditions. These projects aim to demonstrate the reliability and performance of hydrogen technology and gather data for future deployments.
- Long-Haul Potential: Suitable for long-distance trucking.
- Fast Refueling: Minimizes downtime for commercial vehicles.
- Reduced Emissions: Significant reduction in air pollutants and greenhouse gases.
The successful deployment of hydrogen fuel cell technology in heavy-duty transportation requires collaboration between vehicle manufacturers, fuel suppliers, and government agencies. Supportive policies and incentives will be essential to accelerate the adoption of hydrogen fuel cell trucks and buses across the country.
The Role of Government Incentives
Government incentives play a pivotal role in encouraging the adoption of hydrogen fuel cell technology in the heavy-duty transportation sector. Tax credits, subsidies, and grants can help offset the higher upfront costs of hydrogen vehicles and refueling infrastructure, making them more competitive with traditional fossil fuel options.
Hydrogen Fuel Cells in Public Transportation
Public transportation agencies are increasingly seeking sustainable solutions to reduce their environmental impact. Hydrogen fuel cell buses offer a pathway to achieve zero-emission public transportation.
This helps to improve air quality in urban areas.
Benefits for Bus Fleets
Hydrogen fuel cell buses provide the same benefits as fuel cell trucks, including zero emissions and long ranges. They also offer a quieter and smoother ride for passengers, enhancing the overall public transportation experience.
Case Studies and Examples
Several cities in the US have already deployed hydrogen fuel cell buses as part of their public transportation fleets. These deployments demonstrate the viability of hydrogen technology in urban transit and pave the way for broader adoption.
- Urban Air Quality: Reduces air pollution in cities.
- Quiet Operation: Enhances passenger comfort.
- Sustainable Transit: Contributes to a greener public transportation system.
The transition to hydrogen fuel cell buses requires a coordinated effort between transit agencies, vehicle manufacturers, and hydrogen suppliers. Public-private partnerships can facilitate the deployment of hydrogen infrastructure and the procurement of fuel cell buses.
Hydrogen Fuel Cells for Passenger Vehicles
While battery-electric vehicles have gained significant market share in the passenger vehicle segment, hydrogen fuel cell vehicles offer a complementary option for consumers who prioritize longer ranges and faster refueling.
They also address concerns about battery range anxiety.
Advantages for Consumers
Hydrogen fuel cell cars can travel longer distances on a single tank of fuel compared to many battery-electric vehicles. Refueling takes only a few minutes, similar to gasoline cars, which can be particularly appealing to consumers who value convenience.
Market Availability and Models
Currently, there are a limited number of hydrogen fuel cell car models available in the US market. These models are primarily sold or leased in California, where hydrogen refueling infrastructure is more developed.
- Longer Range: Addresses range anxiety for consumers.
- Fast Refueling: Provides convenience comparable to gasoline cars.
- Zero Emissions: Contributes to cleaner air and reduced greenhouse gas emissions.
The future of hydrogen fuel cell passenger vehicles depends on expanding the refueling infrastructure and reducing the cost of fuel cell technology. Increased consumer awareness and government incentives can also play a role in driving adoption.

Challenges and Opportunities for Hydrogen Fuel Cell Adoption
Despite the numerous benefits, the widespread adoption of hydrogen fuel cells in US transportation faces several challenges. Overcoming these hurdles is crucial to realizing the full potential of hydrogen technology.
But these challenges also present opportunities for innovation.
Cost Reduction
One of the biggest challenges is the high cost of hydrogen fuel cell technology. Reducing the cost of fuel cell components, hydrogen production, and refueling infrastructure is essential to making hydrogen vehicles more competitive with traditional and battery-electric options.
Infrastructure Expansion
Expanding the hydrogen refueling infrastructure is critical to supporting the adoption of hydrogen fuel cell vehicles. This requires significant investment from both the public and private sectors.
Public Awareness and Education
Many consumers and businesses are still unfamiliar with hydrogen fuel cell technology. Raising public awareness and educating people about the benefits of hydrogen vehicles can help drive demand.
- Innovation: Continued R&D is needed.
- Policy: Supportive policies are essential.
- Collaboration: Public-private partnerships can accelerate progress.
By addressing these challenges and capitalizing on emerging opportunities, the US can unlock the full potential of hydrogen fuel cells and pave the way for a cleaner, more sustainable transportation future.
| Key Point | Brief Description |
|---|---|
| 🚀 Zero Emissions | Hydrogen fuel cells produce only water, reducing air pollution. |
| ⛽ Fast Refueling | Vehicles refuel quickly, similar to gasoline cars. |
| 🛣️ Longer Range | Offers extended driving range compared to some EVs. |
| 💰 Cost Challenges | High costs of infrastructure and fuel cell technology need to be reduced. |
FAQ
▼
Hydrogen fuel cells offer zero emissions, high efficiency, and longer driving ranges compared to some alternative fuel technologies, contributing to cleaner air and reduced greenhouse gas emissions.
▼
Most hydrogen refueling stations are located in California, driven by the state’s supportive policies. However, other states are gradually starting to invest in hydrogen infrastructure.
▼
Key challenges include the high cost of hydrogen fuel cell technology, the limited availability of refueling infrastructure, and the need for increased public awareness and education about hydrogen fuel cells.
▼
Hydrogen fuel cell vehicles offer longer ranges and faster refueling times, while battery-electric vehicles have a more established infrastructure and lower fuel costs, depending on electricity prices.
▼
Government incentives, like tax credits and subsidies, can significantly encourage the adoption of hydrogen fuel cell technology by offsetting the higher upfront costs of vehicles and infrastructure development.
Conclusion
In conclusion, while hydrogen fuel cells present a promising pathway to transform US transportation by 2025, achieving widespread adoption requires addressing key challenges related to cost, infrastructure development, and public awareness. Through continued innovation, supportive policies, and collaborative efforts, hydrogen fuel cells could play a significant role in creating a cleaner and more sustainable transportation future.