Algae Biofuels: US Breakthroughs and Commercialization Potential

Algae biofuels represent a promising renewable energy source with the potential to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and decrease reliance on fossil fuels in the US, driven by recent technological advancements and increasing commercialization efforts.
The quest for sustainable energy solutions has led researchers and entrepreneurs to explore diverse alternatives, with understanding the potential of algae biofuels: recent breakthroughs and commercialization prospects in the US emerging as a particularly promising area. Algae’s ability to efficiently capture carbon dioxide and convert it into lipids, which can then be processed into biofuels, has positioned it as a potential game-changer in the renewable energy landscape.
The Allure of Algae Biofuels
Algae biofuels offer several advantages over traditional biofuels derived from crops like corn or soybeans. This section explores these key benefits.
Algae boast a significantly higher lipid yield per acre compared to terrestrial crops, making them a more efficient feedstock for biofuel production. Furthermore, algae can be cultivated on non-arable land, reducing competition with food crop production. This is crucial for ensuring that biofuel production does not compromise food security.
Algae also excel at carbon capture, absorbing CO2 from the atmosphere or industrial sources during photosynthesis. This process not only helps reduce greenhouse gas emissions but also enhances algae growth and lipid production. Additionally, the wastewater treatment capabilities of some algae species contribute to a more sustainable and circular economy.

Enhanced Lipid Production
Researchers are constantly exploring ways to improve lipid production in algae. Genetic engineering, metabolic engineering, and optimized cultivation techniques are all contributing to higher yields.
Carbon Sequestration Benefits
The ability of algae to sequester carbon dioxide is a major environmental advantage. This aspect is particularly attractive to industries seeking to reduce their carbon footprint.
- Algae can absorb CO2 directly from industrial sources, such as power plants.
- This process reduces greenhouse gas emissions.
- The captured CO2 can be used to enhance algae growth.
- Integration with carbon capture technologies offers synergistic solutions.
In conclusion, the allure of algae biofuels lies in their high lipid yield, non-arable land use, and carbon capture capabilities. These advantages position algae as a promising feedstock for sustainable biofuel production.
Recent Breakthroughs in Algae Biofuel Technology
Recent years have witnessed significant technological advancements that are driving down the costs and improving the efficiency of algae biofuel production. This section highlights several of these breakthroughs.
Improved cultivation methods, such as photobioreactors and open pond systems, are enhancing algae growth rates and lipid accumulation. Advanced extraction techniques, like cell disruption using ultrasonic methods and solvent extraction, are streamlining the lipid recovery process.
Genetic engineering is also playing a crucial role, with scientists modifying algae strains to produce higher lipid yields and improved growth characteristics. Furthermore, developments in biorefinery technologies are enabling the conversion of algae biomass into a range of biofuels, including biodiesel, bio jet fuel, and bioethanol.
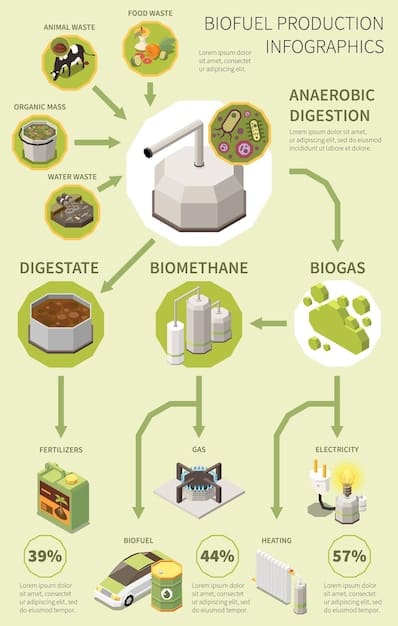
Optimized Cultivation Techniques
Innovative cultivation methods are crucial for scaling up algae biofuel production. Photobioreactors, with their controlled environments, offer higher yields but are more expensive, while open pond systems are cheaper but less efficient.
Genetic Engineering Advances
Genetic engineering holds the key to unlocking the full potential of algae. Modifying algae at the genetic level can lead to the development of strains that produce significantly more lipids.
- Researchers are identifying and manipulating key genes involved in lipid biosynthesis.
- Genetic modifications can enhance algae growth rates and nutrient uptake.
- Strain selection and improvement are essential for optimizing biofuel production.
- Genome editing tools like CRISPR offer precise control over genetic modifications.
In summary, technological advancements in cultivation methods, extraction techniques, and genetic engineering are significantly enhancing the efficiency and economic viability of algae biofuel production.
Commercialization Prospects in the US
Despite the technological progress, commercializing algae biofuels in the US still faces several challenges. This section examines the current state of the industry and the prospects for widespread adoption.
High production costs, regulatory hurdles, and competition from established biofuel sources remain significant barriers. However, strategic partnerships between algae biofuel companies, government agencies, and private investors are helping to overcome these challenges. Pilot-scale and demonstration projects are being implemented across the US to validate the economic and environmental benefits of algae biofuels.
Government incentives, such as tax credits and research grants, are also playing a vital role in supporting the nascent algae biofuel industry. As technologies mature and economies of scale are achieved, algae biofuels are expected to become increasingly competitive in the renewable energy market.
Regulatory Landscape
Navigating the regulatory landscape is crucial for algae biofuel commercialization. Compliance with environmental regulations and obtaining necessary permits can be complex and time-consuming.
Investment and Funding
Securing sufficient investment is critical for scaling up algae biofuel production. Government funding, private equity, and venture capital are all important sources of financing.
- Public-private partnerships can leverage resources and expertise.
- Government grants and tax incentives can stimulate investment.
- Attracting venture capital requires demonstrating technological and economic viability.
- Long-term returns on investment are essential for sustained growth.
In conclusion, while commercializing algae biofuels in the US faces challenges, strategic partnerships, government incentives, and ongoing technological advancements are paving the way for widespread adoption.
Environmental and Economic Considerations
The long-term viability of algae biofuels hinges on their environmental and economic performance. This section delves into these crucial considerations.
Life cycle assessments are essential for evaluating the environmental impacts of algae biofuel production, from cultivation to combustion. Factors such as energy consumption, greenhouse gas emissions, and water usage need to be carefully analyzed. Economic feasibility studies are also crucial for determining the cost competitiveness of algae biofuels compared to fossil fuels and other renewable energy sources.
Innovations in biorefinery processes and waste valorization, such as converting algae biomass into valuable co-products, can significantly improve the economic and environmental sustainability of algae biofuel production. By optimizing resource utilization and minimizing waste, algae biofuels can contribute to a more circular and sustainable economy.
Water Usage Efficiency
Water availability is a major concern for algae biofuel production, particularly in arid regions. Developing water-efficient cultivation systems and utilizing wastewater sources can mitigate this challenge.
Co-Product Development
Extracting valuable co-products from algae biomass can enhance the economic viability of biofuel production. This includes products like animal feed, bioplastics, and nutraceuticals.
- Integrating co-product development into the biorefinery process can increase revenue streams.
- Co-products can offset the production costs of biofuels.
- Valorizing waste streams can reduce environmental impacts.
- Sustainable co-product development is essential for a circular economy.
In summary, careful consideration of environmental impacts and economic feasibility is essential for the long-term viability of algae biofuels. Innovations in biorefinery processes and waste valorization can enhance both the economic and environmental sustainability of algae biofuel production.
Policy and Regulatory Support for Algae Biofuels
Supportive policies and regulations are essential for fostering the growth of the algae biofuel industry. This section examines the role of government in promoting algae biofuel development.
Government initiatives, such as the Renewable Fuel Standard (RFS), provide mandates and incentives for the use of biofuels, including algae biofuels. Tax credits, research grants, and loan guarantees can further stimulate investment and innovation in the industry.
Collaboration between government agencies, research institutions, and private companies is crucial for accelerating the development and commercialization of algae biofuels. Addressing regulatory barriers and creating a level playing field for algae biofuels can help unlock their full potential as a sustainable energy source.
Incentives and Subsidies
Government incentives and subsidies can help offset the higher production costs of algae biofuels and make them more competitive with fossil fuels.
Research and Development Funding
Investing in research and development is crucial for advancing algae biofuel technology. Government funding can support basic and applied research, as well as pilot-scale and demonstration projects.
- Public funding can foster innovation and attract private investment.
- Collaborative research projects can accelerate the pace of technology development.
- Investing in workforce development can ensure a skilled labor pool for the industry.
- Long-term research funding is essential for sustained progress.
In conclusion, government policies and regulations play a crucial role in supporting the development and commercialization of algae biofuels. Incentives, research funding, and collaborative initiatives can help create a favorable environment for the growth of the industry.
Future Trends and Opportunities
The future of algae biofuels is bright, with several emerging trends and opportunities shaping the industry. This section explores these exciting prospects.
Continued advancements in genetic engineering, biorefinery technologies, and sustainable cultivation practices are expected to further reduce production costs and improve the efficiency of algae biofuel production. Integration with carbon capture technologies and wastewater treatment systems will enhance the environmental benefits of algae biofuels.
The development of new and innovative applications for algae biomass, such as bioplastics and high-value chemicals, will also create new revenue streams and diversify the algae biofuel industry. As the world transitions towards a more sustainable energy future, algae biofuels are poised to play an increasingly important role in the renewable energy mix.
Integration with Carbon Capture and Storage
Integrating algae biofuel production with carbon capture and storage (CCS) technologies can create a closed-loop system that significantly reduces greenhouse gas emissions.
Development of High-Value Co-products
Producing high-value co-products from algae biomass can enhance the economic viability of biofuel production and diversify the industry.
- Algae can be used to produce bioplastics, nutraceuticals, and animal feed.
- Co-product development can create new revenue streams.
- Valorizing waste streams can reduce environmental impacts.
- Sustainable co-product development is essential for a circular economy.
In summary, the future of algae biofuels is promising, driven by continued technological advancements, integration with carbon capture technologies, and the development of high-value co-products. As the world transitions towards a more sustainable energy future, algae biofuels are poised to play an increasingly important role.
| Key Point | Brief Description |
|---|---|
| 🌱 High Lipid Yield | Algae produce more oil per acre than traditional crops. |
| ♻️ Carbon Capture | Algae absorb CO2, reducing greenhouse gas emissions. |
| 🔬 Genetic Advances | Genetic engineering improves algae lipid production. |
| 💰 Commercialization Challenges | High costs and regulations hinder widespread adoption. |
FAQ About Algae Biofuels
▼
Algae biofuels are biofuels derived from algae biomass. Algae can be cultivated to produce lipids, which are then converted into biodiesel, bio jet fuel, and other biofuels, offering a sustainable alternative to fossil fuels.
▼
Algae biofuels offer several advantages. They have a higher lipid yield compared to traditional crops, can be grown on non-arable land, and absorb CO2. This makes them a more sustainable and efficient biofuel source.
▼
The main challenges include high production costs, regulatory hurdles, and competition from established biofuels. However, technological advancements and supportive policies are helping to overcome these challenges.
▼
The US government supports algae biofuels through initiatives like the Renewable Fuel Standard, tax credits, research grants, and loan guarantees. These measures stimulate investment and innovation in the industry.
▼
The future of algae biofuels is promising. Continued advancements in technology, integration with carbon capture, and the development of high-value co-products are expected to drive the industry forward, making algae biofuels an important part of the renewable energy mix.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the potential of algae biofuels: recent breakthroughs and commercialization prospects in the US reveals a promising pathway towards a sustainable energy future. While challenges remain, ongoing advancements and strategic support are paving the way for algae biofuels to play an increasingly significant role in the renewable energy landscape.





